
This information shows that at the present level of operating sales (200 units), the change from this level has a DOL of 6 times. Next, if the case toggle is set to “Upside”, we can see that revenue is growing 10% each year and from Year 1 to Year 5, and the company’s operating margin expands from 40.0% to 55.8%. Just like the 1st example we had for a company with high DOL, we can see the benefits of DOL from the margin expansion of 15.8% throughout the forecast period. In the final section, we’ll go through an example projection of a company with a high fixed cost structure and calculate the DOL using the 1st formula from earlier. In addition, in this scenario, the selling price per unit is set to $50.00, and the cost per unit is $20.00, which comes out to a contribution margin of $300mm in the base case (and 60% margin).
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Both tools are used by businesses to increase operating profits and acquire additional assets, respectively. For example, a software company has higher fixed costs (i.e., salaries) since the majority of their expenses are with developing the actual software–not producing it. But, if something happens to the economy, that software company how to make a chart of accounts would have a hard time paying their high fixed costs. A DOL of 2.68 means that for every 10% increase in the company’s sales, operating income is expected to grow by 26.8%. This is a big difference from Stocky’s—which grows 10.9% for every 10% increase in sales. There are two operating leverage formulas that are the most popular.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
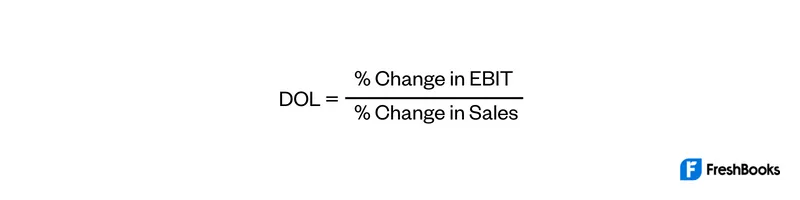
The revenues of company XYZ are $ 58.6 million, and that of company LMN are $ 32.7 million. The variable costs of company XYZ and company LMN are $25.7 million and $14.56 million. Similarly, the fixed costs of company XYZ and company LMN are $10.9 million and $6.54 million.
Degree of Operating Leverage Formula
Since profits increase with volume, returns tend to be higher if volume is increased. The challenge that this type of business structure presents is that it also means that there will be serious declines in earnings if sales fall off. This does not only impact current Cash Flow, but it may also affect future Cash Flow as well. In our example, we are going to assess a company with a high DOL under three different scenarios of units sold (the sales volume metric). If revenue increased, the benefit to operating margin would be greater, but if it were to decrease, the margins of the company could potentially face significant downward pressure. Where Q is the quantity, P is price, V is variable cost per unit and FC is fixed cost.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
On the flip side, if there’s an upturn in sales—and most of your costs stay the same—you stand to gain substantial profit. Because if sales drop, most likely your variable costs will drop too since they are used for production. A measure of this leverage effect is referred to as the degree of operating leverage (DOL), which shows the extent to which operating profits change as sales volume changes. This indicates the expected response in profits if sales volumes change.
Regardless of whether revenue increases or decreases, the margins of the company tend to stay within the same range. A second approach to calculating DOL involves dividing the % contribution margin by the % operating margin. Company C’s case shows that degree of operating leverage is not a constant, but it depends on the output level. Another accounting term closely relates to the degree of operating leverage.
We will discuss each of those situations because it is crucial to understand how to interpret it as much as it is to know the operating leverage factor figure. 11 Financial is a registered investment adviser located in Lufkin, Texas. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. The degree of combined leverage gives any business the optimal level of DOL and DOF.
Running a business incurs a lot of costs, and not all these costs are variable. In other words, there are some costs that have to be paid even if the company has no sales. These types of expenses are called fixed costs, and this is where Operating Leverage comes from.
- We will need to get the EBIT and the USD sales for the two consecutive periods we want to analyze.
- The financial leverage ratio divides the % change in sales by the % change in earnings per share (EPS).
- On the other side, a higher proportion of variable costs will lead to a low operating leverage ratio and a lower profit from each additional sale for the company.
- For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
A company with high financial leverage is riskier because it can struggle to make interest payments if sales fall. Read on as we take a closer look at the degree of operating leverage. We’ll go over exactly what it is, the formula used to calculate it, and how it compares to the combined leverage. By analyzing DOL, stakeholders can better anticipate the impacts of sales fluctuations on a company’s profitability. We put this example on purpose because it shows us the worst and most confusing scenario for the operating leverage ratio. For illustration, let’s say a software company has invested $10 million into development and marketing for its latest application program, which sells for $45 per copy.
When sales increase, a company with high operating leverage can see significant boosts in operating income due to the fixed nature of its costs. Conversely, if sales decline, the company still needs to cover substantial fixed costs, which can significantly hurt profitability. If fixed costs are high, a company will find it difficult to manage short-term revenue fluctuation, because expenses are incurred regardless of sales levels.
As said above, we can verify that a positive operating leverage ratio does not always mean that the company is growing. Actually, it can mean that the business is deteriorating or going through a bad economic cycle like the one from the 2nd quarter of 2020. It lets businesses gain significant profits on every progressive sale. On the contrary, companies having low operating leverage may find it effortless to earn a profit when trading with lower sales. It is important to understand the concept of the DOL formula because it helps a company appreciate the effects of operating leverage on the probable earnings of the company.
